Learning Labs are interactive, focused, and supported learning sessions where you can learn how to implement Langara’s teaching and learning technologies and tools. Capacity is limited to ensure all attendees have an opportunity to ask questions, try out tools, and receive support. Support in the room will reflect the technology, tool, and learning outcomes; however, you can expect to interact with EdTech Advisors, Specialists, and Technologists as well as TCDC Curriculum Consultants. The Labs are an opportunity to implement something new or improve what already exists with experts who can answer technical questions and provide advice.
Fall Learning Lab session topics include:
After participating in this lab, participants should be able to:
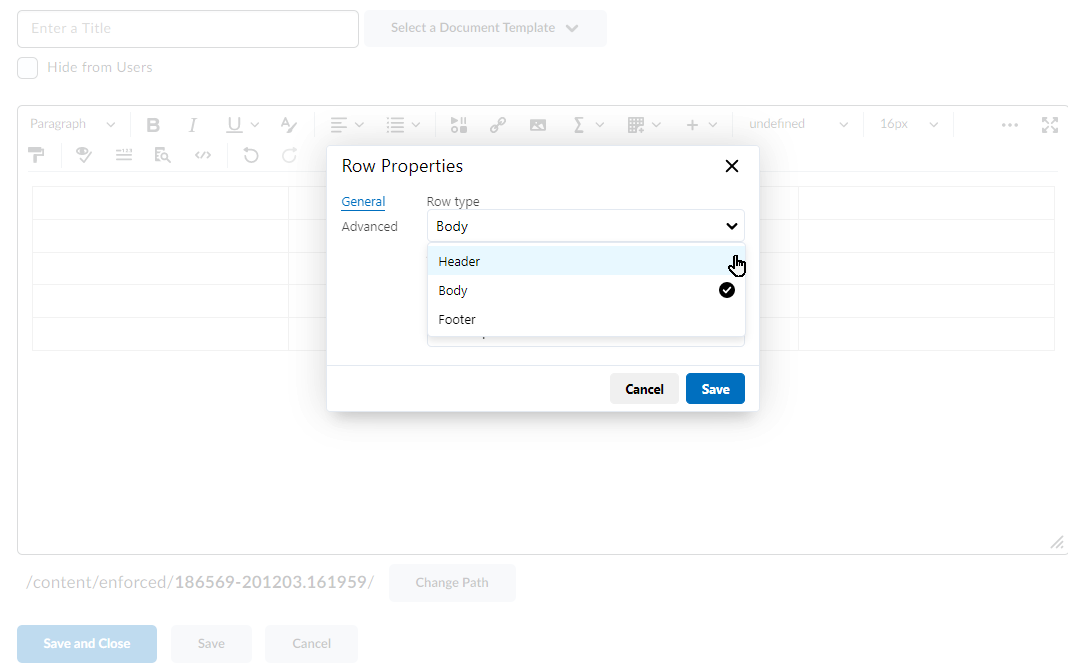
- Use the Brightspace HTML editor.
- Explain the benefits of using the Brightspace HTML templates.
- Apply the templates to a new Brightspace HTML page.
- Apply the latest version of the template to an existing Brightspace HTML page.
- Mix and match HTML elements—such as image placement, accordions, callouts, tables, and tabs—from the various templates.
Adding closed captions to a video in Brightspace
After participating in this lab, participants should be able to:
- Upload a video to MediaSpace.
- Add closed captions to a video.
- Use the MediaSpace captions editor.
- Use the OneDrive captioning tool.
- Embed a video in a Brightspace course file.
Creating an accessible Word document
After participating in this lab, participants should be able to:
- Employ plain language.
- Select styles that improve legibility of text.
- Structure a document.
- Create accessible hyperlinks and tables.
- Add alternative text to visual content.
- Use the built-in accessibility checker.
Improving the accessibility of existing PowerPoint slides
After participating in this lab, participants should be able to:
- Avoid the most common PowerPoint accessibility mistakes.
- Use the accessibility checker and make corrections.
- Apply templates.
- Apply structure.
- Select accessible fonts and font styling.
- Employ accessible use of colour.
- Add alternative text to images.
- Write meaningful hyperlink text.
Save time marking with Rubrics
After participating in this lab, participants should be able to:
- Define the purpose of the assignment or assessment
- Decide which type of rubric will be used with assignments
- Create statements of expected performance at each level of the rubric
- Transfer analog rubrics into a digital version on Brightspace
- Associate their rubric with the assignment in Brightspace






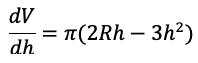
 Brightspace is an excellent tool to provide equitable, inclusive access to course content, documents, and media.
Brightspace is an excellent tool to provide equitable, inclusive access to course content, documents, and media.