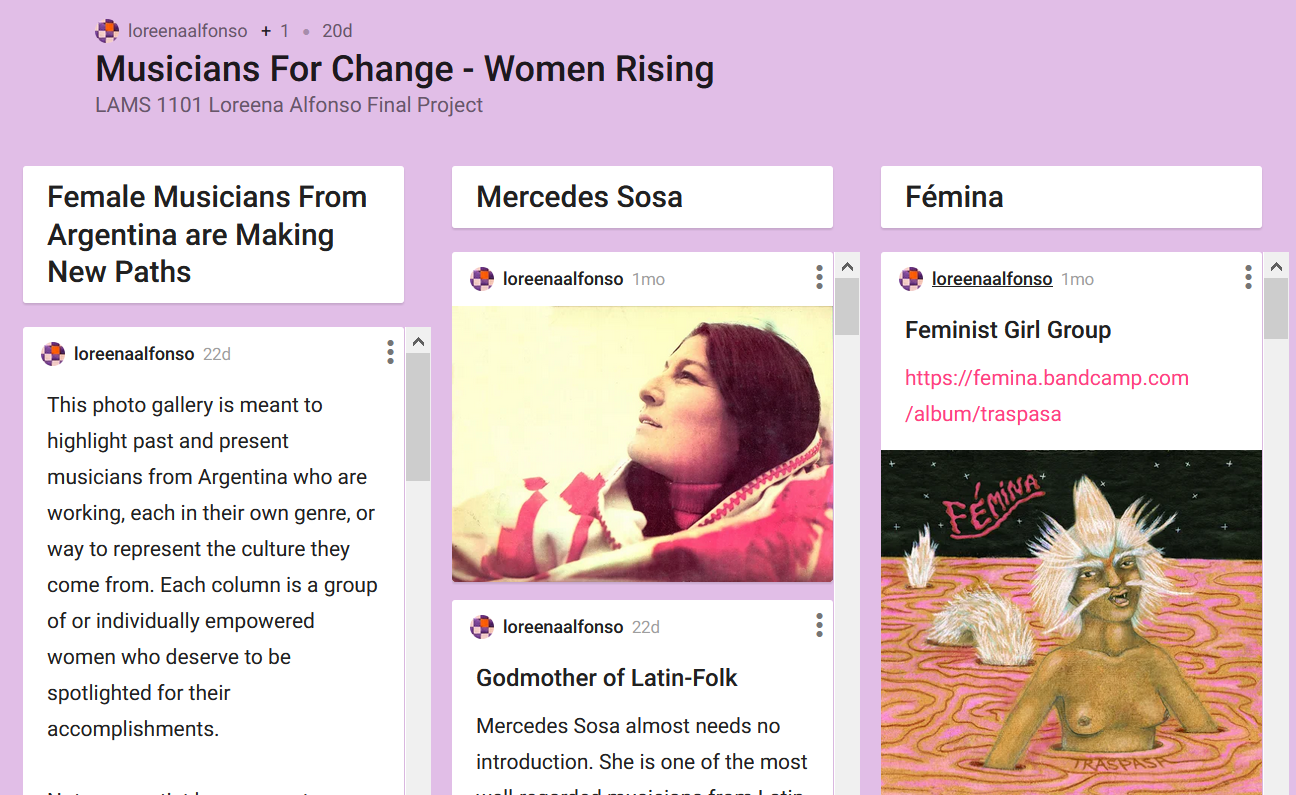
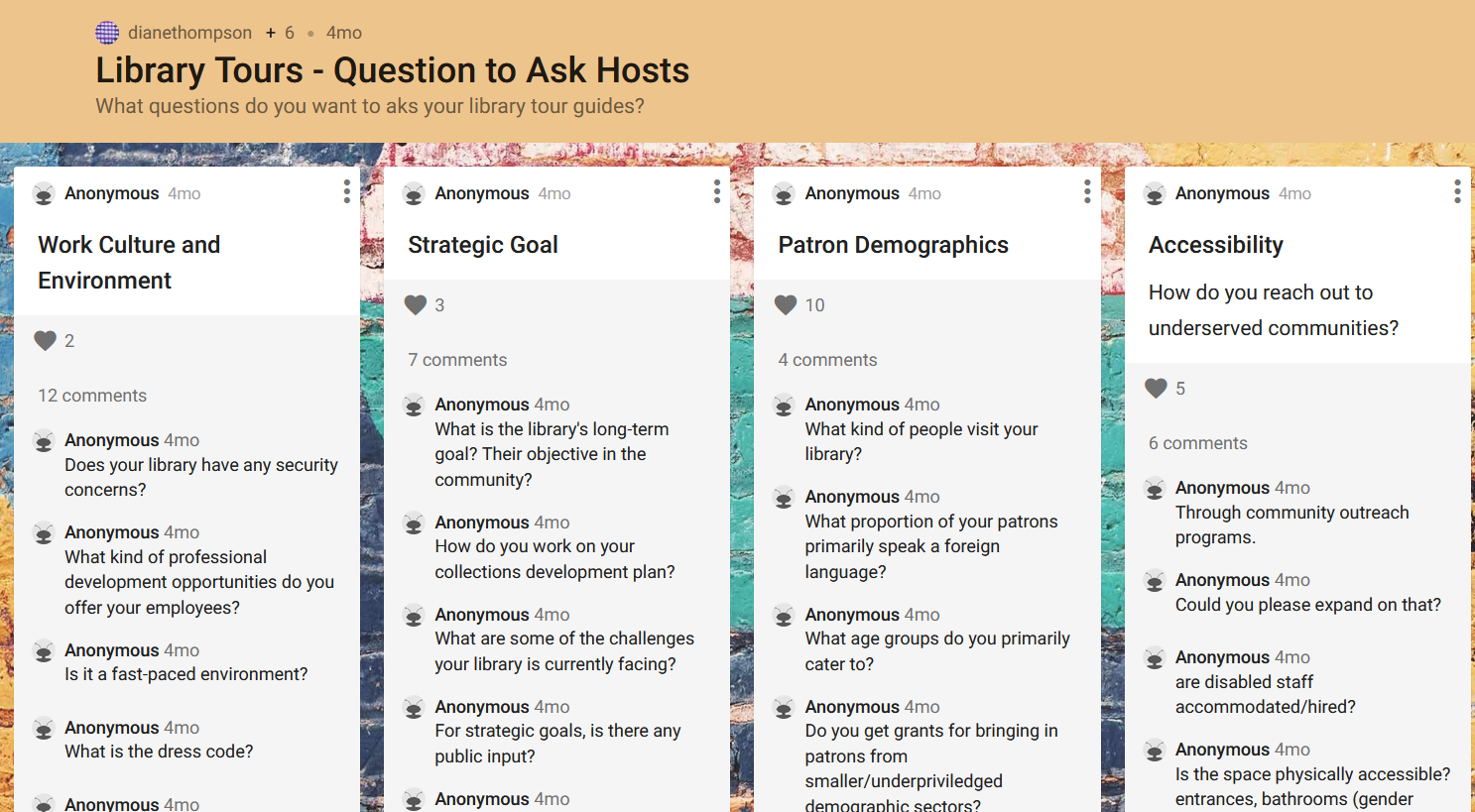
What is PebblePad*?

PebblePad is Langara’s online portfolio and experiential learning platform. Digital portfolios, or ePortfolios, are powerful tools for learning, assessment, and career development because they enable users to document their skills, learning, and creativity, as well as reflect on what/how/why they learn. Using PebblePad, students can create portfolios, blogs, basic webpages, online collections of files, formal and informal reflections, action plans, and more. For authentic and scaffolded experiential learning, PebblePad is also a great fit.
How Might it Be Used Within a Course or Formal Learning Experience?
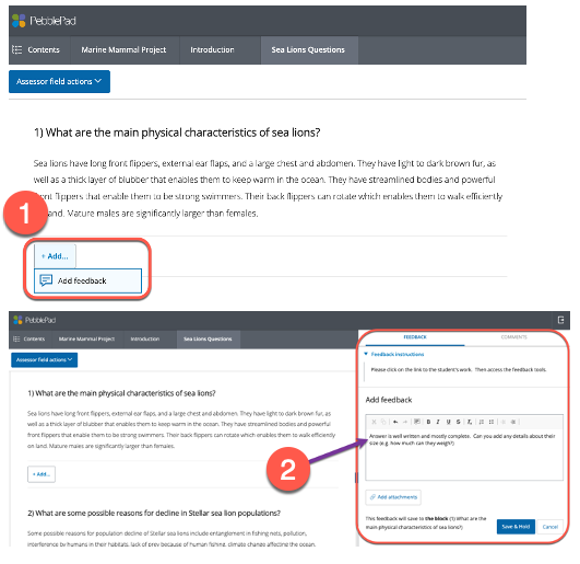
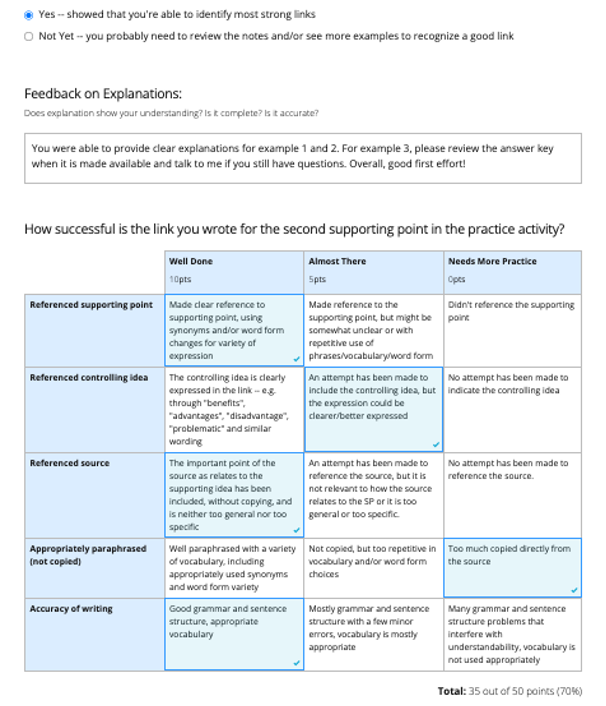
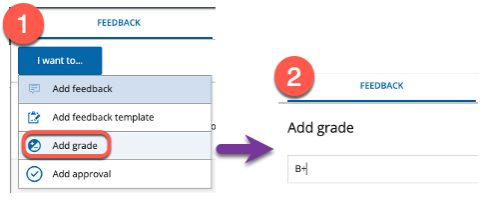
PebblePad is being used in many practicum and clinical courses at Langara. Students use interactive digital workbooks to document their experiences and demonstrate what they have learned. Links to these workbook assignments are then shared with faculty for feedback and assessment.
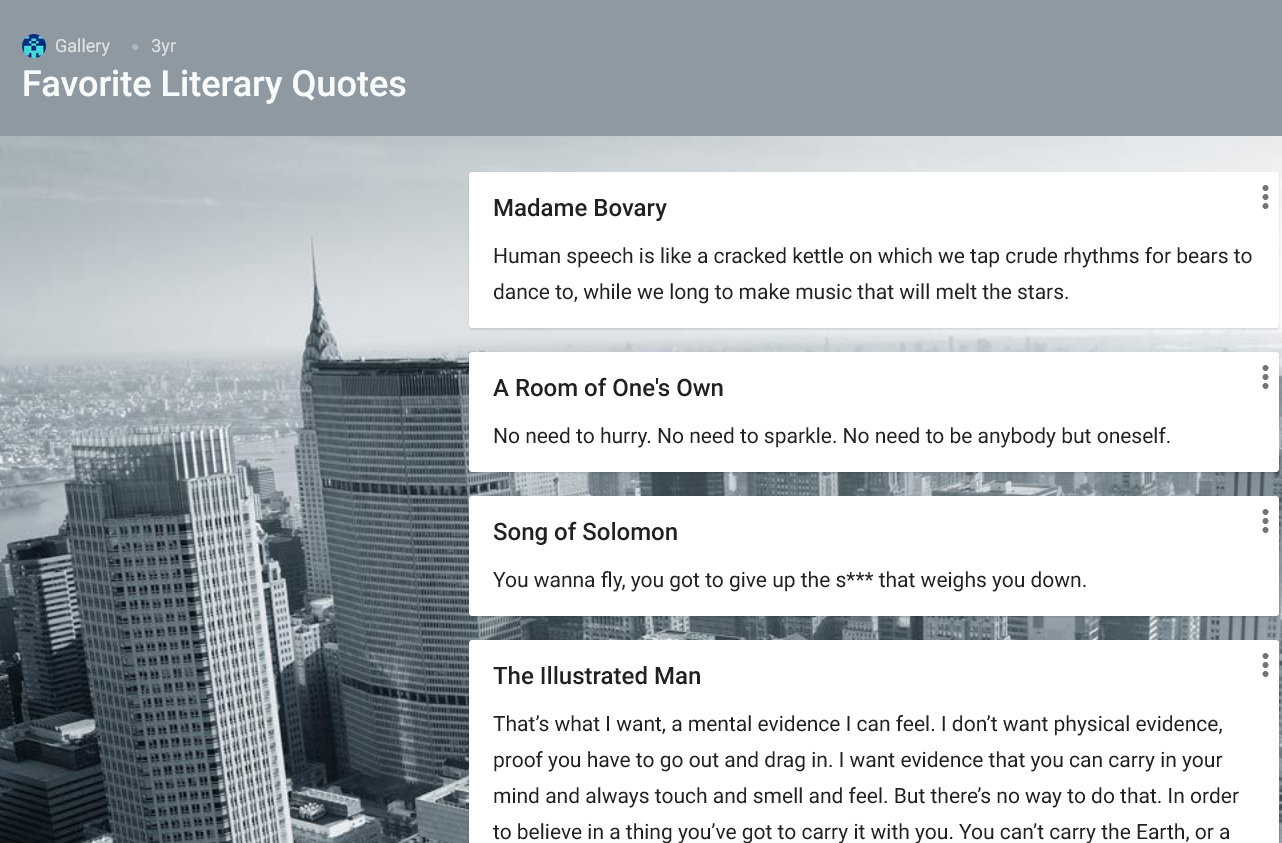
For programs where students have more open-ended and/or creative assignments, classic portfolios can be created on PebblePad where students document, showcase, and reflect on their creative work. This type of assignment empowers students to design and collate content ranging from text and hyperlinks, to images and video.
To find out more about the possibilities, we encourage you to go to the PebblePad Community Learner Showcase to explore some of the work being done at other institutions.
Why Use PebblePad?
PebblePad is student-owned. Once a student takes a course using PebblePad, they will be issued a PebblePad account that they will have for their entire time at Langara and beyond. This makes it a great tool for them to make connections across their learning journey, and it can support the transition to further studies or employment.
Research indicates that using digital portfolios like PebblePad within courses and programs also seems to advance student retention and success (Eynon, Gambino, & Török, 2014). Proponents theorize that ePortfolios are beneficial because they support learning in the following ways:
- learning can be made visible, including through reflection activities
- connections can be made across and between academic (course, program), extracurricular (work experience, volunteering), and personal (family, community life) learning
- personal, academic, and professional identity construction can be supported
- social pedagogies can be employed, supporting group work, peer feedback, mentorship, etc.
- competencies – within and outside of formal academic courses – can be documented and assessed
Want to Learn More?
If you are interested in learning more about PebblePad, contact EdTech to talk to an Advisor. Please also check the EdTech calendar for upcoming workshops.
Email edtech@langara.ca for more information.
*PebblePad is now the preferred ePortfolio technology of BCNET.
References
Blake Yancey, K. (Ed.). (2019). ePortfolio as Curriculum: Models and Practices for Developing Students’ ePortfolio Literacy. Sterling, VA: Stylus.
Eynon, B., & Gambino, L.M. (2017). High-Impact ePortfolio Practice: A Catalyst for Student, Faculty, and Institutional Learning. Sterling, VA: Stylus.
Eynon, B., Gambino, L. M., & Török, J. (2014). What difference can ePortfolio make? A field report from the Connect to Learning Project. International Journal of ePortfolio, 4(1), 95-114. https://www.theijep.com/pdf/IJEP127.pdf
Penny Light, T., Chen, H., & Ittelson, J. (2011). Documenting learning with ePortfolios: A guide for college instructors. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass.
Watson, C. E., Kuh, G. D., Rhodes, T., Light, T. P., & Chen, H. L. (2016). Editorial: ePortfolios – The Eleventh High Impact Practice. International Journal of EPortfolio, 6(2), 65–69.
Yeo, N., & Rowley, J. (2020). ‘Putting on a Show’ Non-Placement WIL in the Performing Arts: Documenting Professional Rehearsal and Performance Using Eportfolio Reflections. Journal of University Teaching & Learning Practice, 17(4).