As part of Open Education week, I recently attended a workshop at Kwantlen Polytechnic University with Paul Stacey, Associate Director of Global Learning at the non-profit organization Creative Commons. Previously at SFU and BC Campus, Paul has been instrumental in driving the adoption of OER (Open Educational Resources) in the BC post-secondary sector.
Rather than give a traditional presentation, Paul adopted a more informal question and answer session with approximately thirty workshop participants. He started by explaining what Creative Commons licenses are and stressed they are still a form of copyright attached to a creative work. The difference between “all rights reserved” copyright and Creative Commons licenses is that under the latter the author stipulates a set of permissions so that others can use a creative work in certain ways under certain conditions. Unlike “all rights reserved” copyright, Creative Commons licenses are “some rights reserved:” they allow creativity while ensuring the author retains ownership rights over the work.
The licenses themselves are best thought of as being on a ‘permissiveness’ continuum from the most permissive and open (Public Domain marks and CC BY – Attribution) through to the least permissive (CC BY NC ND). Paul, along with organisations like JISC, advocates for the use of CC BY wherever possible. The different licenses themselves are explained very well on the Creative Commons website. There is also a great License Chooser Tool if you are unsure which license to use. Although earlier versions of CC licenses were country/region specific, the new version 4.0 can be applied globally regardless of geographical location.
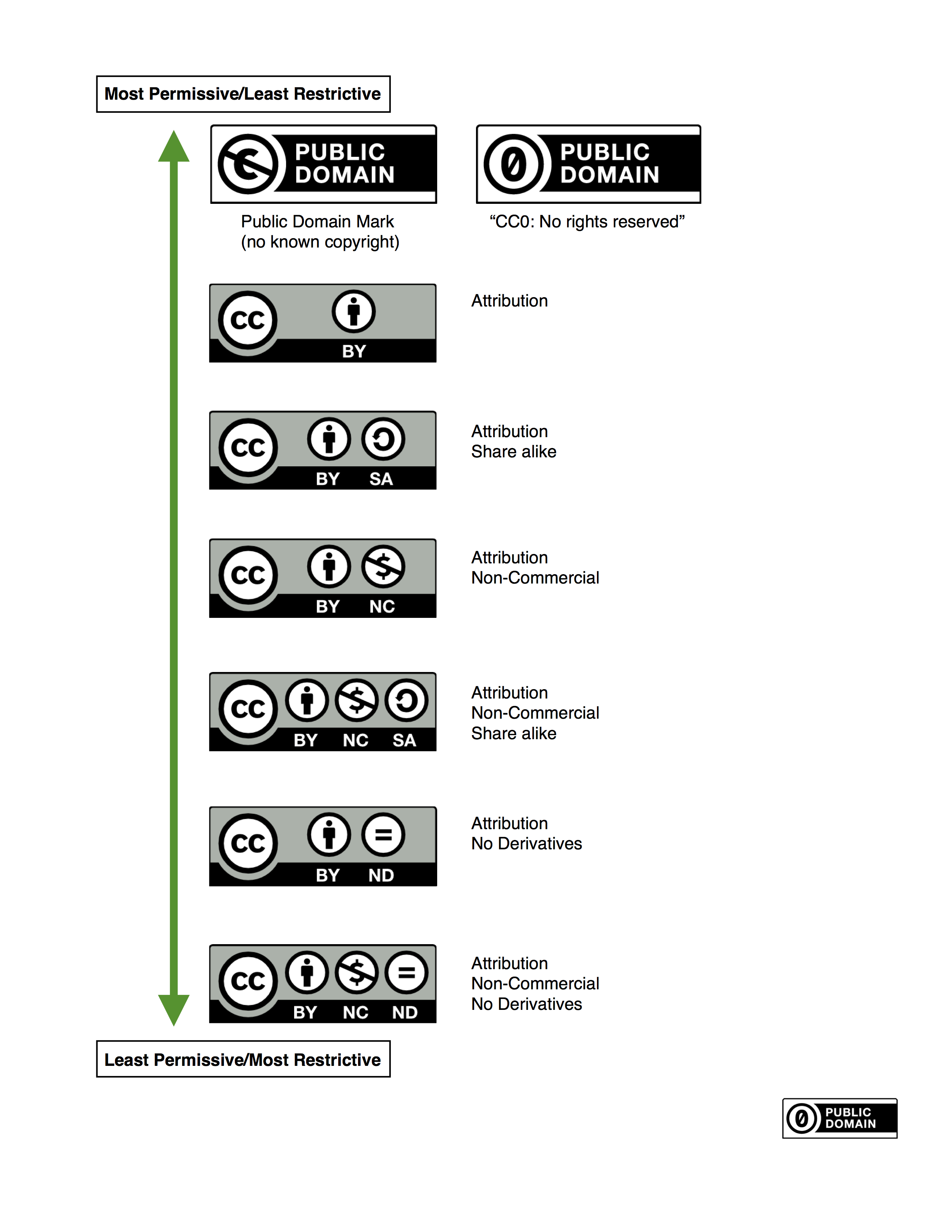
Paul went on to demonstrate some real-world examples of the licenses in practice. The Librivox Free Audiobook Collection provides free audio recordings of books in the public domain. Similarly German-Japanese pianist Kimiko Ishizaka’s interpretation of Bach’s Open Goldberg Variations has been made available under a CC0 (zero) Public Domain license, meaning that any use can be made of the work without even the need for attribution. CC BY (Attribution) licenses are used by the OpenStax Textbook project and CC BY SA (Attribution, Share-alike) is used by Wikipedia. The board game Cards Against Humanity uses CC BY NC SA, online journal The Conversation uses CC BY ND and an example of the least permissive CC BY NC ND license is provided by the Teach AIDS website.
Openly licensing educational content has many benefits. Paul mentioned some of the more obvious ones such as the cost-savings to students of faculty adopting an open textbook, or the higher quality resources resulting from a collaborative peer authoring and review process. Beyond this, however, it is important to remember the core values of education that open educational practices support. Sharing and building on the ideas of others is fundamental to public education, as are academic freedom and innovation in teaching practice. Open textbooks, for example, increase academic freedom by taking control away from publishers and putting the potential to re-purpose and re-mix directly in the hands of faculty and students. Think, for example, of the exciting opportunities that exist to adapt textbooks for local contexts and update the content more regularly than traditional textbooks. Or think of the pedagogical innovations that might occur when we invite students to co-produce a classroom text?
Finally, Paul covered some important considerations when starting out with OER and open textbooks at an institution. Make sure you adopt a bottom-up as well as top-down approach, i.e get both senior management and faculty/student buy-in. Have a look around to see what exists already – at Langara, for example, we already have faculty in Physics and Math using open textbooks with their students; we’re not starting from scratch. Think about how OER will be stored, curated and distributed/shared. And have a clear institutional strategy that involves as many internal stakeholders as possible, while taking advantage of the ever-expanding wealth of resources and networks that are available in the open education space.
Julian Prior (Educational Technology Advisor)


 ion. Should we really expect students to pay tuition fees and buy textbooks and then to pay a subscription fee so that they can take the quizzes? We believe that more instructors should be aware of Socrative.
ion. Should we really expect students to pay tuition fees and buy textbooks and then to pay a subscription fee so that they can take the quizzes? We believe that more instructors should be aware of Socrative.

