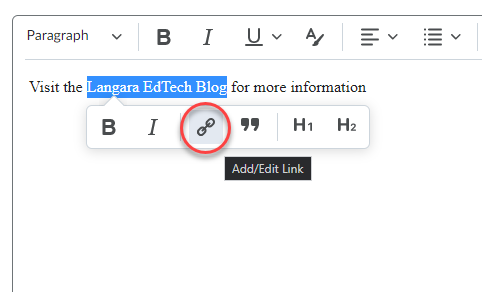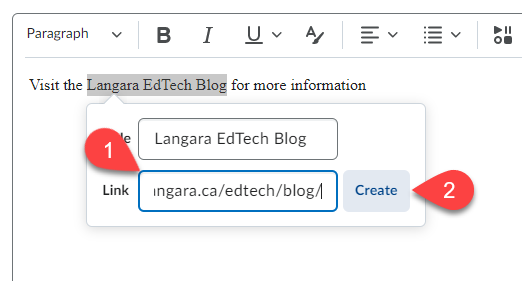
Whether you are a superuser or a novice, the number of resources on generative artificial intelligence can be overwhelming. EdTech and TCDC have curated some that we’d like to recommend.
- How to access Copilot (Microsoft)
- Interested in trying a generative AI tool or using it in your course? ChatGPT and Copilot (formerly Bing Chat) are currently available in Canada. Langara College students and employees have access to a premium version of Copilot through Microsoft Enterprise and the Edge browser. Microsoft’s FAQs provide information on how to access Copilot through Microsoft Edge.
- Practical AI for Instructors and Students (Ethan Mollick/Wharton School, August 2023)
- If you’re looking for a great primer on AI, this series of five videos is worth the watch. Each video is approximately 10 minutes so the whole series can be viewed in under an hour. Topics include: 1) an introduction to AI; 2) what large language model (LLM) platforms like ChatGPT are and how to start using them; 3) how to prompt AI; 4) how instructors can leverage AI; and 5) how students can use AI.
- Note: this series references four LLMs: ChatGPT, BingCopilot, Bard, and Claude. Bard and Claude are not yet available in Canada.
- AI Primer by Educause
- This article is a reading (and viewing) list that links to resources that do a deeper dive into generative AI. A good resource for those who know the basics and would like to learn more.
- Welcome to AI in Education (University of Sydney)
- This is the University of Sydney’s AI resource for students. It can also be a good resource for faculty who want to start with the basics. The modules include: Introduction to AI, Prompts to Help You Learn, Prompts to Help you Create, Prompts to Help you Progress, and Guidelines for Using Generative AI.
- Incorporating AI in Learning Assessments: A Guided Pathway (Sean McMinn, June 2023)
- This dynamic flowchart can be a guide for educators who are interested in incorporating AI tools into assessment activities. According to the creators, the chart “begins with a decision on AI usage, then splits into two routes: one explores the pedagogical impact and appropriate use of AI tools, while the other offers a range of traditional assessment techniques. The chart emphasizes ethical considerations, academic integrity, and equal tool access throughout.”
- What to do about assessments if we can’t out-design or out-run AI? (Danny Liu and Adam Bridgeman, University of Sydney, July 2023)
- Are Your Students Ready for AI?: A Four-Step Framework to Prepare Learners for a ChatGPT World (Oguz A. Acar, Harvard Business Publishing, June 2023)
- A short read that’s practical and clear. The article argues that students will be using generative AI in their careers and outlines a framework on how to prepare them.
- Advancing Meaningful Learning in the age of AI (Oregon State University Ecampus)
- This article reconsiders Bloom’s Taxonomy given the existence of AI.
- AI-generated misinformation: 3 teachable skills to help address it (Jaigris Hodson, The Conversation, October 2023)
- An introduction to prompting generative AI like ChatGPT for teaching and learning (Seb Dianati and Suman Laudari, The Times Higher Education | Inside Higher Education, August 2023)
- Flowchart: Quick Start Guide for Using Artificial Intelligence (UBC)
- UBC adapted this flowchart from a UNESCO resource and is designed to help students approach AI use with academic integrity.
EdTech and TCDC also regularly offer professional learning opportunities on AI topics. Check the PD Events Calendar for current offerings.
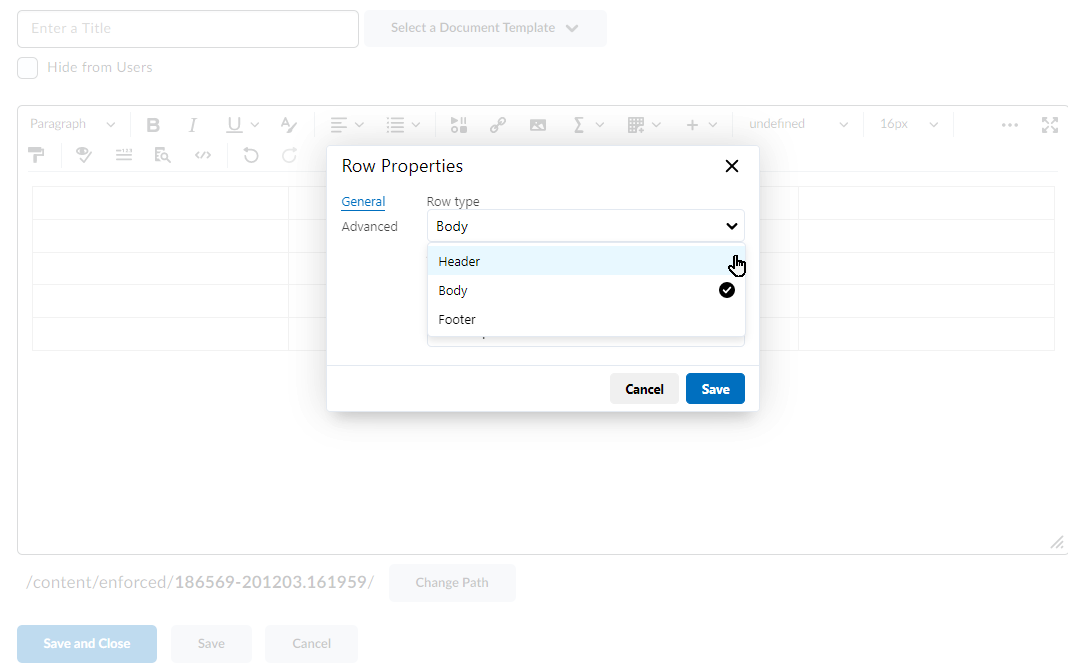
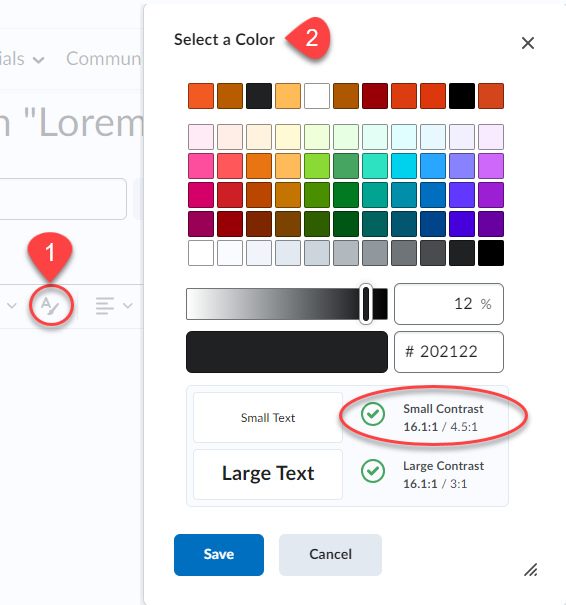
As always, if you’re planning to integrate AI into your course, please be aware that:
- There are privacy concerns with AI platforms. We recommend using caution when inputting – or having your students input – private, personal, or sensitive information (e.g. resumes or other identifying data).
- For those using assistive technology such as screen readers, some AI platforms are more accessible than others. For more information, please see Accessibility of AI Interfaces by Langara Assistive Technologist, Luke McKnight.
If you would like more recommendations for AI resources, or any other AI-related support, please contact EdTech or TCDC.

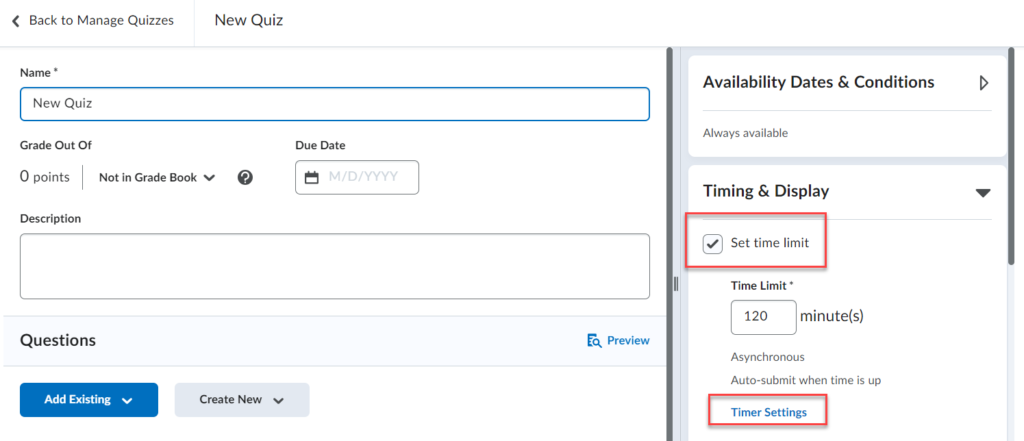
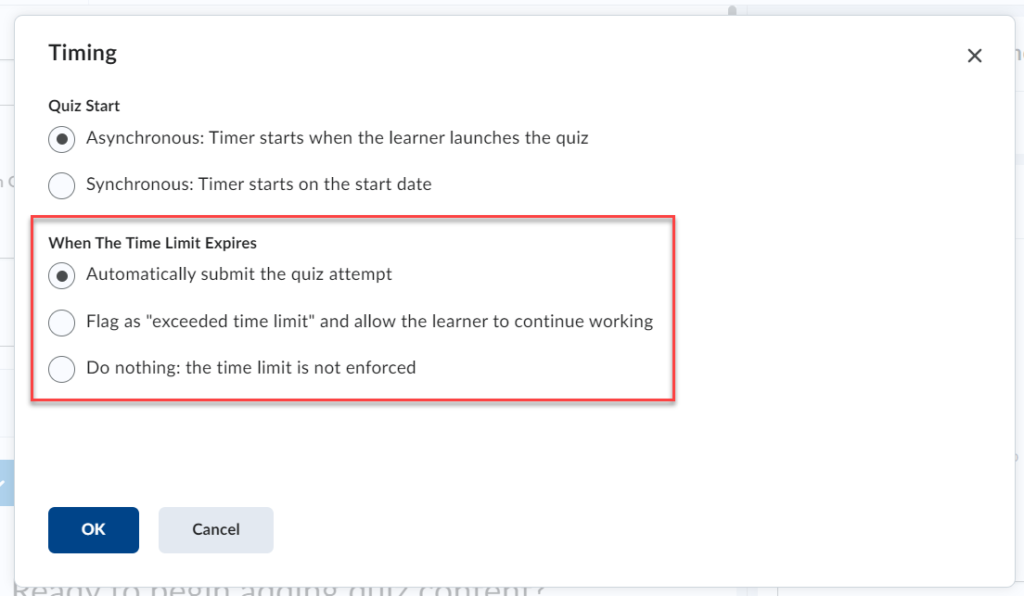
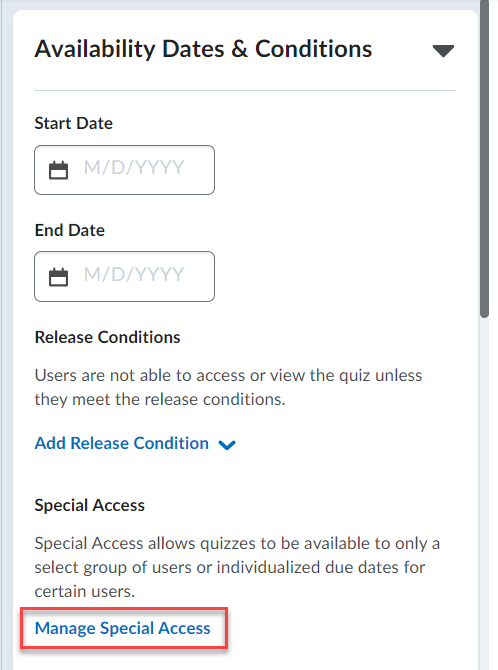

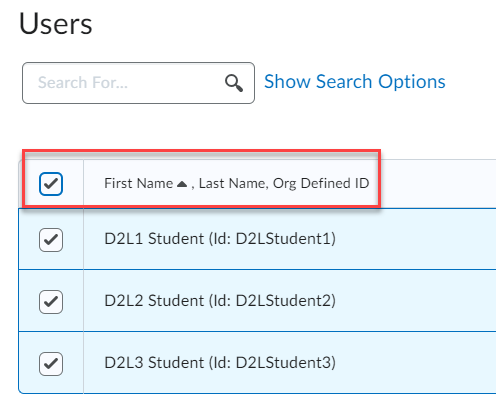





 Brightspace is an excellent tool to provide equitable, inclusive access to course content, documents, and media.
Brightspace is an excellent tool to provide equitable, inclusive access to course content, documents, and media.